December 1, 2023
Product Sourcing Company: Finding the Best Suppliers for Your Business
Product sourcing companies and agents play a crucial role in helping businesses find the best products at the best prices.
Read MoreDecember 1, 2023
Product sourcing companies and agents play a crucial role in helping businesses find the best products at the best prices.
Read MoreNovember 30, 2023
Setting up a fashion label can be a daunting task, but with the right knowledge and resources, it can be
Read MoreNovember 30, 2023
Outsourcing and procurement are two terms that are often used interchangeably in business, but they actually refer to two different
Read More
November 27, 2023
A tech pack is a crucial document for any fashion designer or manufacturer looking to produce high-quality garments. It serves
Read More
November 23, 2023
CNF meaning in export is a crucial term that every importer and exporter should understand. CNF refers to Cost and
Read MoreNovember 5, 2023
Apple Inc. is a multinational technology company that designs, develops, and sells consumer electronics, computer software, and online services. The
Read More
November 5, 2023
When importing goods into a country, it is important to understand when duty payments are required. Duty is a tariff
Read More
November 1, 2023
HTS code lookup is an essential process for businesses and individuals involved in international trade. The Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS)
Read More
December 18, 2021
Do you want to know about inspection tools and how these can be used? Go nowhere else as we have
Read More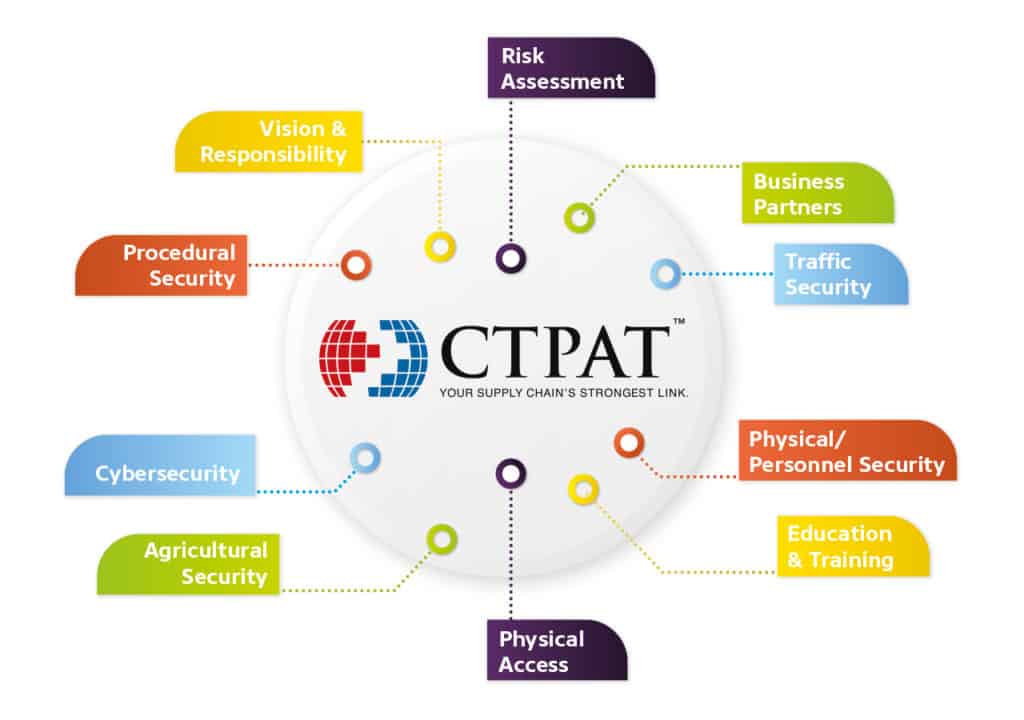
October 22, 2021
Have you ever heard about C TPAT AUDIT? If yes, you can move on to other sites, but if that’s
Read More